How do turbochargers work?
A turbocharger is a device that increases an engine's power and efficiency by forcing more air into the engine's combustion chamber. Here's how a turbocharger works:
-
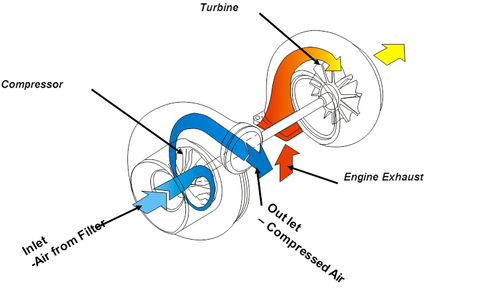
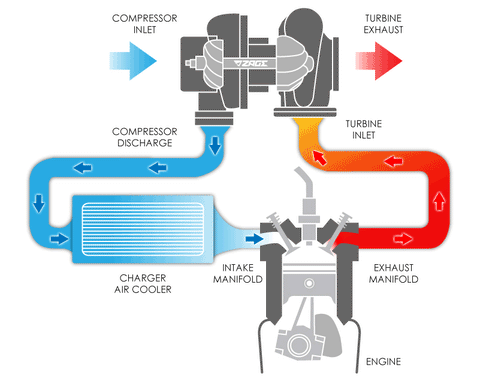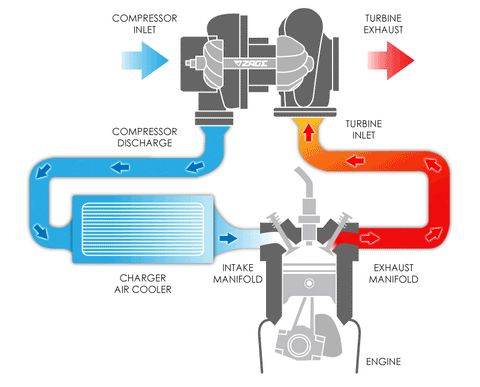
Exhaust Gases: The turbocharger is powered by the engine's exhaust gases. As the exhaust gases flow out of the engine's cylinders, they pass through the turbine side of the turbocharger.
-
Turbine Wheel: The exhaust gases spin a turbine wheel, which is connected to a shaft.
-
Compressor Wheel: On the other end of the shaft, there is a compressor wheel. As the turbine wheel spins the shaft, it also spins the compressor wheel.
-
Compressed Air: The spinning compressor wheel draws in fresh air and compresses it, which increases its density.
-
Intercooling: In most turbocharged engines, the compressed air is often routed through an intercooler to cool it down before it enters the engine. Cooler air is denser and can help improve combustion efficiency.
-
Boosted Air Intake: The compressed air is then forced into the engine's intake manifold, increasing the air pressure in the combustion chamber.
-
More Fuel and Power: With more air in the combustion chamber, the engine can burn more fuel efficiently, producing more power as a result.
The increased air and fuel mixture in the engine results in a higher power output compared to a naturally aspirated engine of the same size. Turbocharging also helps improve the engine's efficiency and fuel economy by optimizing the combustion process.
Overall, the turbocharger uses the engine's exhaust gases to drive a turbine, which in turn drives a compressor that forces more air into the engine, resulting in increased power and performance.